Industry 4.0 Series – Part 5 – Industry 4.0 Technologies – Advanced Robots
In today’s world, technological advancements are profoundly transforming numerous sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare, logistics to defense. One of the key pillars of this transformation is advanced robotics technology. Equipped with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), sensor technologies, and automation systems, these robots enhance human capabilities, providing faster, more efficient, and safer solutions.
The rise of Industry 4.0 and autonomous systems has enabled robots to evolve beyond mere machines that perform repetitive tasks. They can now make decisions, perceive their surroundings, and adapt to changing conditions. A surgical robot, for instance, can perform operations with micro-precision without damaging the patient’s tissues, while a logistics robot can organize warehouse shelves within seconds.
Before diving deeper, let’s take a look at the historical development of robotics.
The Meaning and Origin of the Word “Robot”
The word “robot” was first used in 1920 by Czech writer Karel Čapek in his science fiction play R.U.R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots). It is derived from the Czech word “robota,” which means “forced labor” or “drudgery.”
Unimate
Unimate was the world’s first industrial robot. It was used in 1961 at General Motors’ factory in New Jersey for hot die-casting operations.
Invented by George Devol in the 1950s, Unimate’s patent application was filed in 1954 and granted in 1961. Devol, along with his business partner Joseph Engelberger, founded Unimation, the world’s first robotics manufacturing company.

Unimate’s success led to the growth of the industrial robotics market. In the 1970s, companies such as KUKA, ABB, Fanuc, and Yaskawa began manufacturing robots.
Features of Advanced Robots
- Sensors and Cameras
Sensors and perception systems enable robots to see their surroundings, collect data, and analyze information. Technologies such as infrared sensors, cameras, and radar systems allow robots to detect objects, avoid obstacles, and even recognize faces.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Through data collection, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) enable robots to analyze and interpret data. This allows them to quickly adapt to new conditions, predict possible scenarios, and make real-time decisions based on processed data.
- Advantages
Speed: Robots can keep up with demanding work schedules. They always operate faster than humans and do not experience fatigue, ensuring continuous efficiency in production.
Repeatability: Robots can consistently produce the same results every time. Their repeatability surpasses human capability, making them highly advantageous, especially in assembly lines.
Precision: From precision manufacturing to surgical operations, robots ensure that repetitive tasks are performed with minimal tolerance and variability.
Safety: In hazardous environments, advanced robots can take on risky tasks that humans would otherwise have to perform, enhancing workplace safety.
Advanced Robots
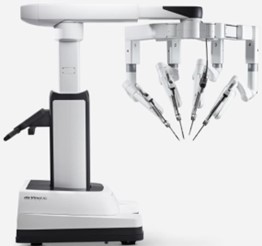
Da Vinci – Healthcare
The Da Vinci Robot is a revolutionary surgical system used in the healthcare sector, particularly in robotic surgery. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, this system helps surgeons perform minimally invasive (small incision) surgeries with high precision.
What is a Cobot? (Collaborative Robot) – Manufacturing
A cobot is a shortened form of “collaborative robot.” It refers to robots designed to work safely alongside humans. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots can directly interact with human operators without the need for safety barriers.
The first true collaborative robot was produced in 2008 by Universal Robots.
Leading Cobot Manufacturers:
Universal Robots (UR) – The company that developed the first cobot.
ABB – Known for its YuMi cobot model.
Fanuc – Produces the CR series collaborative robots.
KUKA – Offers flexible cobot solutions with the LBR iiwa model.

Kiva – Amazon Robots – Logistics
Amazon’s logistics robots are advanced technology systems used to speed up e-commerce operations, increase efficiency, and support human labor. In 2012, Amazon took a major step into robotic logistics by acquiring Kiva Systems, and since then, it has continuously advanced its robotics technology. Kiva robots are designed to transport product shelves and enhance movement within warehouses. This technology is widely known in the industry as AGV.
AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle)
AGVs, or Automated Guided Vehicles, are driverless logistics vehicles used to optimize material handling processes. They operate with navigation systems such as sensors, cameras, laser guidance, or magnetic strips.
KİVA
UPS Flight Forward – Drone Delivery
UPS Flight Forward is a drone delivery service developed by United Parcel Service (UPS). In 2019, it became the first drone delivery company to receive full certification from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) technology, UPS Flight Forward aims to provide fast, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly deliveries. This service is particularly valuable for hospitals, pharmaceutical distribution centers, and urgent logistics needs.
Tesla Optimus
Tesla Optimus – Manufacturing & Household Tasks
Tesla Optimus is a humanoid robot developed by Tesla, designed to automate physical tasks. Elon Musk has stated that this robot will reduce reliance on human labor, boost productivity, and become a cornerstone of the robotic workforce in the future.
Key Features of Tesla Optimus:
Humanoid Design: Stands 1.73 meters tall, weighs approximately 57 kg, and mimics human movements with a bipedal structure.
Tesla AI Technology: Powered by the same artificial intelligence used in Tesla’s autonomous driving technology.
Energy Efficiency: Equipped with a battery system similar to Tesla vehicle batteries, integrated into its chest.
Advanced Mechanical Hands: Capable of precise object handling, gripping, and manipulation.
Vision & Perception Sensors: Uses cameras and sensors to perceive its environment and navigate autonomously.
“Robots won’t take our jobs; they will make our work more meaningful for us.” Elon Musk
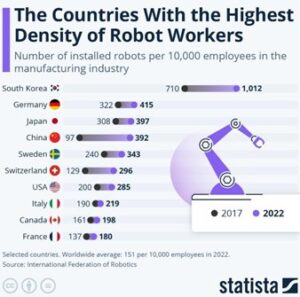
Graph of Countries’ Robot Technologies
I would like to share a graph showing the development of robot technologies in different countries. In this graph, you can see the top 10 countries with the highest robot usage. The graph compares the number of robots per 10,000 employees between 2017 and 2022.
South Korea is significantly ahead compared to other countries.
Final
Advanced robots are more than just machines; they expand human limits, unleash creativity, and serve as a gateway to the future. They continue to revolutionize every field, from industry to households, healthcare to space exploration.
However, it should not be forgotten that robots are a product of human intelligence, and the greatest power still lies in human imagination. The future will be built alongside robots, but it will be a future guided by humans.
References
https://standardbots.com/blog/advanced-robotics
https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unimate
https://control.com/technical-articles/origin-story-meet-unimate-the-first-industrial-robot/
https://new.abb.com/products/robotics/robots/collaborative-robots/yumi
https://www.intuitive.com/en-us/products-and-services/da-vinci
https://www.businessinsider.com/amazon-doubled-the-number-of-kiva-robots-2015-10
https://www.digitaltrends.com/news/drone-delivery-breakthrough-for-ups/